應用深度學習模型提升PM2.5濃度預報準確度
Enhancing real-time PM2.5 forecasts: A hybrid approach of WRF-CMAQ model and CNN algorithm
Author: Yi-Ju Lee,Fang-Yi Cheng,Hsiao-Chen Chien,Yuan-Chien Lin,Min-Te Sun
Publication: Atmospheric Environment
Publisher: Elsevier
Date: 1 December 2024
doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2024.120835
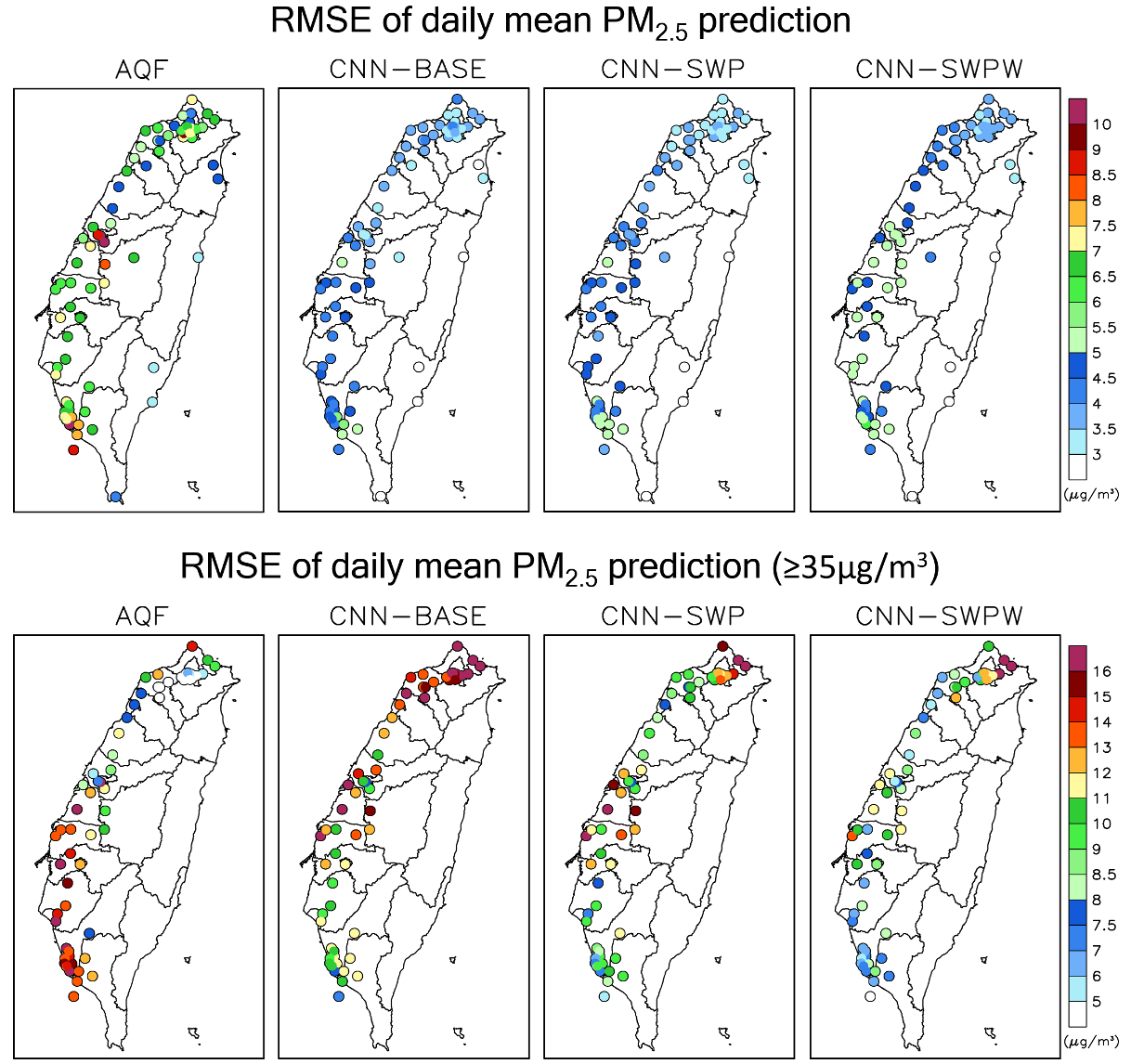
在國科會計畫經費的支持下,我們開發了一個基於卷積神經網絡(CNN)的72小時PM2.5預測模型,旨在提升現有空氣品質預報系統的準確度。該模型的最大特色在於僅使用少量變數作為訓練資料,包含地面逐時PM2.5濃度觀測資料及CMAQ空氣品質預報系統的逐時PM2.5預報資料。除此之外,模型將天氣型態分類(Synoptic Weather Patterns, SWPs)作為唯一的氣象變數,這樣的設計旨在降低預報系統的作業複雜度。
實驗設計中,我們開發了三個不同的CNN模型:CNN-BASE(不含SWPs)、CNN-SWP(含SWPs)以及CNN-SWPW(含SWPs且引入加權損失函數)。結果顯示,這些CNN模型有效提升了基於CMAQ的空氣品質預報系統的準確率,其中分類評估(低、中、高PM2.5濃度)的預報準確率由77%提升至87%。然而,由於高濃度污染事件樣本數較少,CNN-BASE模型在預測高濃度PM2.5時表現欠佳。加入SWPs作為訓練資料後,模型能更準確地反映氣象條件對高污染事件的影響,顯著提升了高濃度PM2.5的預測準確度。此外,CNN-SWPW透過加權損失函數處理樣本數不平衡問題,進一步增強了對高濃度PM2.5的預測能力。
這樣的改進使得我們的模型在低變數情境下,仍能在實際空品預報作業化中保持高效且準確的預測,特別是在高污染事件的預測方面有著顯著的進步。
With the support of funding from the National Science and Technology Council (NSTC), we developed a 72-hour PM2.5 forecasting model based on a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) two years ago, aiming to improve the accuracy of the current air quality forecasting system. The key feature of this model is the use of a minimal number of variables for training, including hourly PM2.5 concentration observations from ground stations and hourly PM2.5 forecasts from the CMAQ air quality forecasting system. In addition, the model uses Synoptic Weather Patterns (SWPs) as the only meteorological variable. This design aims to reduce the operational complexity of the forecasting system.
By incorporating SWPs as training data, the model more accurately captured the influence of meteorological conditions on high-pollution events, significantly improving the prediction accuracy for high PM2.5 concentrations. Moreover, CNN-SWPW further enhanced the accuracy of high PM2.5 predictions by using a weighted loss function to address the issue of sample imbalance.
This improvement allows our model to maintain high efficiency and accuracy in real-time operations, even with a minimal number of variables, and it shows significant progress, especially in forecasting high pollution events.